The LASIMM Project Objectives
The project aimed to develop a Large Additive/Subtractive Integrated Modular Machine (LASIMM) based on a scalable open architecture framework with associated software enabling full parallel manufacturing.
The objectives were based on the major research challenges and were:
- Integration of a seamlessly additive, subtractive, metrology and cold work capability into a single machine featuring an advanced control system;
- Develop the software capability for generation of tool paths and sequences for a parallel process multi-head system;
- Ensure components’ structural integrity by allowing in-process non-destructive testing and repair of defects by layer machining;
- Production of functional parts with the final desired accuracy, surface finish, tolerances and material efficiency;
- Production of components with mechanical properties better than forged material thanks to the unique and innovative adoption of in-process cold-work during additive operations;
- Demonstrate the machines capability by producing test pieces defined by industrial requirements;
- Enable the creation of mixed-material structure using compatible as well as incompatible materials for increased functionality of the part and locally tailored mechanical properties
Benefits
LASIMM offers a perfect opportunity to automate and fully integrate the two additive and subtractive aspects. The specific benefits compared to current practice in metal AM are:
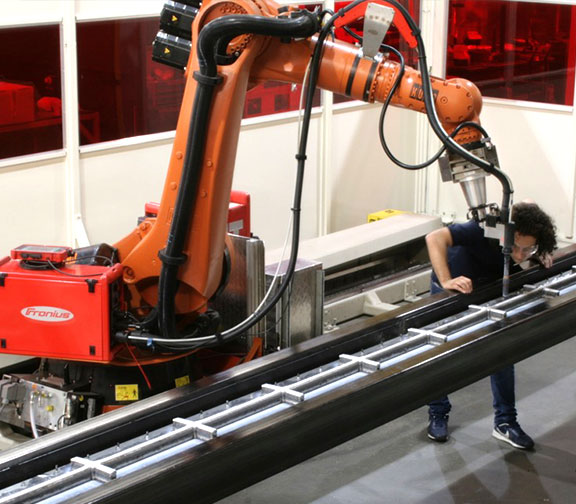

The LASIMM project also contributed to overcome the “Valley of death” regarding the industrial implementation of Hybrid (AM+SM) processes. This was supported by the development of activities related to:
- Standardization: LASIMM partners worked, during the project duration (and after its end), in close collaboration with standardization bodies (e.g. CEN and ISO) with objective of identifying “gaps” in existing standards and addressing them, by reviewing existing standards or by support the development of new standards.
- Training/Qualification of personnel: LASIMM partners also looked at identifying the training needs related to the LASIMM project, this ensured that, at the end of the project, the necessary “tools” for training the LASIMM workforce will be in place.